List of mustelids
Species in mammal family Mustelidae From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Mustelidae is a family of mammals in the order Carnivora, which includes weasels, badgers, otters, ferrets, martens, minks, and wolverines, and many other extant and extinct genera. A member of this family is called a mustelid; Mustelidae is the largest family in Carnivora, and its extant species are divided into eight subfamilies. They are found on all continents except Antarctica and Australia, and are a diverse family; sizes range, including tails, from the widespread 17 cm (7 in) least weasel to the 1.8-meter (6 ft) giant otter of Amazonian South America. Habitats vary widely as well, from the arboreal marten to the fossorial European badger to the marine sea otter. Population sizes are largely unknown, though two species, the sea mink and Japanese otter, were hunted to extinction in 1894 and 1979, respectively, and several other species are endangered. Some species have been domesticated, e.g. the ferret and some populations of the South American tayra. Mustelidae is one of the oldest families in Carnivora; early mustelids first appeared around 28–33 million years ago.[1]

The 23 genera and 62 extant species of Mustelidae are split into 8 subfamilies: Guloninae, martens and wolverines; Helictidinae, ferret-badgers; Ictonychinae, African polecats and grisons; Lutrinae, otters; Melinae, Eurasian badgers; Mellivorinae, the honey badger; Mustelinae, weasels and minks; and Taxidiinae, the American badger. In addition to the extant subfamilies, Mustelidae includes three extinct subfamilies designated as Leptarctinae, Mustelavinae, and Oligobuninae. Extinct species have also been placed into all of the extant subfamilies besides Helictidinae, in both extant and extinct genera; around 200 extinct Mustelidae species have been found, as well as fossil genera not given a species name, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (2 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically endangered (1 species) |
| EN | Endangered (7 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (6 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (7 species) |
| LC | Least concern (39 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (1 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (1 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the mustelid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct species or subspecies listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†". Population figures are rounded to the nearest hundred.
Classification
Summarize
Perspective
The family Mustelidae consists of 62 extant species belonging to 23 genera and divided into hundreds of extant subspecies, as well the extinct sea mink and Japanese otter, which are the only mustelid species to become extinct since prehistoric times. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species. Modern molecular studies indicate that the 23 genera can be grouped into 8 subfamilies. Some prior classification schemes divided the family solely between the aquatic otters and all other species.
Subfamily Guloninae (Martens and wolverines)
- Genus Eira: one species
- Genus Gulo: one species
- Genus Martes: seven species
- Genus Pekania: one species
Subfamily Helictidinae (Ferret-badgers)
- Genus Melogale: five species
Subfamily Ictonychinae (African polecats and grisons)
- Genus Galictis: two species
- Genus Ictonyx: two species
- Genus Lyncodon: one species
- Genus Poecilogale: one species
- Genus Vormela: one species
Subfamily Lutrinae (Otters)
Subfamily Melinae (Eurasian badgers)
Subfamily Mellivorinae (Honey badger)
- Genus Mellivora: one species
Subfamily Mustelinae (Weasels and minks)
Subfamily Taxidiinae (American badger)
- Genus Taxidea: one species
Mustelids
Summarize
Perspective
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis; this includes reclassifying Guloninae, Helictidinae, Ictonychinae, Melinae, Mellivorinae, and Taxidiinae as subfamilies rather than as part of a paraphyletic group with Mustelinae
Subfamily Guloninae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tayra | E. barbara (Linnaeus, 1758) Seven subspecies
|
Central America, Trinidad in the Caribbean, and northern South America |
Size: 60–70 cm (24–28 in) long, plus 35–45 cm (14–18 in) tail[2] Habitat: Forest and savanna[3] Diet: Primarily eats fruit, carrion, small vertebrates, insects, and honey[3] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolverine | G. gulo (Linnaeus, 1758) Two subspecies
|
Arctic North America, Europe, and Asia |
Size: 70–105 cm (28–41 in) long, plus 18–26 cm (7–10 in) tail[4] Habitat: Rocky areas, shrubland, forest, and grassland[5] Diet: Primarily eats carrion and small to large mammals[5] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American marten | M. americana (Turton, 1806) Fourteen subspecies
|
Northern North America (includes range of Pacific marten) |
Size: 46–66 cm (18–26 in) long, plus 13–16 cm (5–6 in) tail[6] Habitat: Forest[7] Diet: Primarily eats rodents and small mammals, as well as birds, insects, fruit, and carrion[7] |
LC
|
| Beech marten | M. foina (Erxleben, 1777) Eleven subspecies
|
Europe and central Asia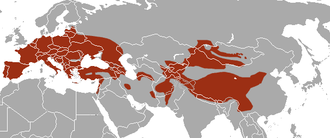 |
Size: 40–50 cm (16–20 in) long, plus 22–30 cm (9–12 in) tail[8] Habitat: Forest, rocky areas, and shrubland[9] Diet: Primarily eats rodents and small mammals, as well as birds, insects, fruit, and carrion[9] |
LC
|
| European pine marten | M. martes (Linnaeus, 1758) Seven subspecies
|
Europe and west Asia |
Size: 48–58 cm (19–23 in) long, plus 16–28 cm (6–11 in) tail[10] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[11] Diet: Primarily eats small mammals, birds, and amphibians, as well as carrion[11] |
LC
|
| Japanese marten | M. melampus (Wagner, 1841) Two subspecies
|
Japan (M. m. melampus in green, M. m. tsuensis in red (Tsushima Island)) |
Size: 47–55 cm (19–22 in) long, plus 17–22 cm (7–9 in) tail[12] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[13] Diet: Primarily eats fruit, small mammals, and insects[13] |
LC
|
| Nilgiri marten | M. gwatkinsii Horsfield, 1851 |
Parts of southern India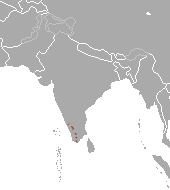 |
Size: 55–65 cm (22–26 in) long, plus 40–45 cm (16–18 in) tail[14] Habitat: Forest and grassland[15] Diet: Primarily eats birds, small mammals, and insects[15] |
VU
|
| Sable | M. zibellina (Linnaeus, 1758) Sixteen subspecies
|
Large parts of Russia |
Size: 38–56 cm (15–22 in) long, plus 9–12 cm (4–5 in) tail[16] Habitat: Forest[17] Diet: Primarily eats small mammals, birds, nuts, and berries[17] |
LC
|
| Yellow-throated marten | M. flavigula (Boddaert, 1785) Nine subspecies
|
Eastern and southeastern Asia |
Size: 50–72 cm (20–28 in) long, plus 33–48 cm (13–19 in) tail[18] Habitat: Forest and grassland[19] Diet: Primarily eats birds, small mammals, and insects[19] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fisher | P. pennanti (Erxleben, 1777) |
Northern North America |
Size: 75–120 cm (30–47 in) long, plus 31–41 cm (12–16 in) tail[20] Habitat: Forest[21] Diet: Primarily eats small to medium mammals, birds, and carrion[21] |
LC
|
Subfamily Helictidinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bornean ferret-badger
|
M. everetti (Thomas, 1895) |
Small parts of Borneo |
Size: 33–44 cm (13–17 in) long, plus 15–23 cm (6–9 in) tail[22] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[23] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates, amphibians, insects, fruit, and carrion[22][23] |
EN
|
| Burmese ferret-badger | M. personata I. Saint-Hilaire, 1831 Five subspecies
|
Southeast Asia |
Size: 33–44 cm (13–17 in) long, plus 15–23 cm (6–9 in) tail[24] Habitat: Grassland, shrubland, and forest[25] Diet: Primarily eats insects and snails, as well as small mammals, frogs, lizards, carrion, birds, eggs, and fruit[24][25] |
LC
|
| Chinese ferret-badger | M. moschata (Gray, 1831) Seven subspecies
|
East Asia |
Size: 30–43 cm (12–17 in) long, plus 15–21 cm (6–8 in) tail[26] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[27] Diet: Primarily eats insects, frogs, and carrion[27] |
LC
|
| Javan ferret-badger | M. orientalis (Blanford, 1888) Two subspecies
|
Parts of Java and Indonesia |
Size: 35–40 cm (14–16 in) long, plus 14–17 cm (6–7 in) tail[28] Habitat: Shrubland and forest[29] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates and insects[28][29] |
LC
|
| Vietnam ferret-badger
|
M. cucphuongensis T. Nadler, 2011 |
Vietnam | Size: Unknown Habitat: Forest[30] Diet: Unknown[30] |
DD
|
Subfamily Ictonychinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greater grison | G. vittata (Schreber, 1776) Four subspecies
|
Northern South America and Central America |
Size: 60–76 cm (24–30 in) long, including tail[31] Habitat: Forest and grassland[32] Diet: Primarily eats small mammals, birds, lizards, amphibians, eggs, and fruit[32] |
LC
|
| Lesser grison | G. cuja (Molina, 1782) Four subspecies
|
Southern South America |
Size: 28–51 cm (11–20 in) long, plus 12–20 cm (5–8 in) tail[33] Habitat: Inland wetlands, forest, grassland, and savanna[34] Diet: Primarily eats small lagomorphs and rodents, as well as birds, frogs, lizards, snakes, and eggs[34] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Striped polecat | I. striatus (Molina, 1782) Nineteen subspecies
|
Central, Southern, and sub-Saharan Africa |
Size: 28–30 cm (11–12 in) long, plus 20–30 cm (8–12 in) tail[35] Habitat: Grassland, savanna, desert, and shrubland[36] Diet: Primarily eats insects[36] |
LC
|
| Saharan striped polecat | I. libycus (Hemprich and Ehrenberg, 1833) Four subspecies
|
Northern, western, and southern edges of the Sahara |
Size: 40–47 cm (16–19 in) long, plus 16–19 cm (6–7 in) tail[37] Habitat: Shrubland and desert[38] Diet: Primarily eats rodents, small mammals, birds, fish, and insects[37][38] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patagonian weasel | L. patagonicus (Blainville, 1842) Two subspecies
|
Argentina |
Size: 30–35 cm (12–14 in) long, plus 6–9 cm (2–4 in) tail[39] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and forest[40] Diet: Primarily eats rodents and birds[40] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African striped weasel | P. albinucha (Gray, 1864) Five subspecies
|
Southern Africa |
Size: 25–36 cm (10–14 in) long, plus 13–23 cm (5–9 in) tail[41] Habitat: Shrubland, forest, savanna, and grassland[42] Diet: Primarily eats small mammals, rodents, and birds, as well as snakes and insects[41][42] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marbled polecat | V. peregusna (Güldenstädt, 1864) Five subspecies
|
Southeast Europe and central Asia |
Size: 28–48 cm (11–19 in) long, plus 14–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[43] Habitat: Desert, rocky areas, grassland, and shrubland[44] Diet: Primarily eats rodents and birds[44] |
VU
|
Subfamily Lutrinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African clawless otter | A. capensis Schinz, 1821 Five subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa |
Size: 72–95 cm (28–37 in) long, plus 40–60 cm (16–24 in) tail[45] Habitat: Forest, inland wetlands, neritic marine, coastal marine, intertidal marine, and grassland[46] Diet: Primarily eats crabs and lobsters, as well as frogs, fish, and insects[45][46] |
NT
|
| Asian small-clawed otter | A. cinereus (Illiger, 1815) Three subspecies
|
Southeast Asia |
Size: 40–63 cm (16–25 in) long, plus 25–35 cm (10–14 in) tail[47] Habitat: Intertidal marine, coastal marine, inland wetlands, forest, shrubland, neritic marine, and grassland[48] Diet: Primarily eats crabs, molluscs, insects, and small fish, as well as rodents, snakes, and amphibians[48] |
VU
|
| Congo clawless otter | A. congicus (Lönnberg, 1910) |
Sub-Saharan Africa |
Size: 79–95 cm (31–37 in) long, plus 50–56 cm (20–22 in) tail[49] Habitat: Forest, inland wetlands, and marine[50] Diet: Unknown[50] |
NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea otter | E. lutris (Linnaeus, 1758) Three subspecies
|
Northern Pacific coasts |
Size: 55–130 cm (22–51 in) long, plus 12–33 cm (5–13 in) tail[51] Habitat: Neritic marine and oceanic marine[52] Diet: Primarily eats marine invertebrates, as well as fish[52] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spotted-necked otter | H. maculicollis (Lichtenstein, 1835) |
Much of sub-Saharan Africa |
Size: 57–69 cm (22–27 in) long, plus 33–44 cm (13–17 in) tail[53] Habitat: Inland wetlands, neritic marine, forest, coastal marine, and intertidal marine[54] Diet: Primarily eats frogs, crabs and small water birds[53][54] |
NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North American river otter | L. canadensis (Schreber, 1777) Seven subspecies
|
United States and Canada, possibly Mexico |
Size: 66–107 cm (26–42 in) long, plus 31–46 cm (12–18 in) tail[55] Habitat: Inland wetlands, intertidal marine, neritic marine, and coastal marine[56] Diet: Primarily eats fish, as well as amphibians and crustaceans[56] |
LC
|
| Southern river otter | L. provocax (Thomas, 1908) |
Southern Chile and Argentina |
Size: 57–70 cm (22–28 in) long, plus 35–46 cm (14–18 in) tail[57] Habitat: Inland wetlands, coastal marine, neritic marine, and intertidal marine[58] Diet: Primarily eats fish and crustaceans[58] |
EN
|
| Neotropical otter | L. longicaudis (Olfers, 1818) Three subspecies
|
South and Central America, Trinidad in the Caribbean |
Size: 50–79 cm (20–31 in) long, plus 37–57 cm (15–22 in) tail[59] Habitat: Coastal marine, inland wetlands, neritic marine, and intertidal marine[60] Diet: Primarily eats fish, as well as crustaceans, insects, amphibians, and molluscs[60] |
NT
|
| Marine otter | L. felina (Molina, 1782) |
West coast of South America |
Size: 57–79 cm (22–31 in) long, plus 30–36 cm (12–14 in) tail[61] Habitat: Coastal marine, intertidal marine, oceanic marine, and neritic marine[62] Diet: Primarily eats crustaceans and molluscs, as well as fish, birds, and small mammals[62] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasian otter | L. lutra (Linnaeus, 1758) Eleven subspecies
|
Europe, North Africa, and large regions of Asia |
Size: 57–70 cm (22–28 in) long, plus 35–40 cm (14–16 in) tail[63] Habitat: Inland wetlands, forest, grassland, coastal marine, neretic marine, intertidal marine, and shrubland[64] Diet: Primarily eats fish, as well as insects, reptiles, amphibians, birds, small mammals, and crustaceans[64] |
NT
|
| Hairy-nosed otter | L. sumatrana (Gray, 1865) |
Scattered parts of southeast Asia |
Size: 50–82 cm (20–32 in) long, plus 35–50 cm (14–20 in) tail[65] Habitat: Inland wetlands, neritic marine, shrubland, grassland, forest, coastal marine, and intertidal marine[66] Diet: Primarily eats fish and water snakes, as well as frogs, lizards, turtles, and crabs[66] |
EN
|
| Japanese otter† | L. nippon Imaizumi, Yoshiyuki, 1989 |
formerly Japan (extinct) | Size: 65–80 cm (26–31 in) long, plus 45–50 cm (18–20 in) tail Habitat: Inland wetlands, neritic marine, shrubland, grassland, forest, coastal marine, and intertidal marine Diet: Fish, crabs, shrimp, eels, beetles, fruit |
EX
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth-coated otter | L. perspicillata Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1826 Three subspecies
|
Iraq, South and southeast Asia |
Size: 65–79 cm (26–31 in) long, plus 40–50 cm (16–20 in) tail[67] Habitat: Inland wetlands, forest, grassland, coastal marine, neritic marine, intertidal marine, and shrubland[68] Diet: Primarily eats fish, as well as shrimp, crabs, and insects[68] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Giant otter | P. brasiliensis (Gmelin, 1788) Two subspecies
|
North and central South America |
Size: 96–123 cm (38–48 in) long, plus 45–65 cm (18–26 in) tail[69] Habitat: Inland wetlands, coastal marine, neritic marine, and forest[70] Diet: Primarily eats fish, as well as caiman and turtles[70] |
EN
|
Subfamily Melinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greater hog badger | A. collaris F. Cuvier, 1825 Four subspecies
|
East and southeast Asia (image includes albogularis and hoevenii) |
Size: 65–104 cm (26–41 in) long, plus 19–29 cm (7–11 in) tail[71] Habitat: Forest, grassland, shrubland, and savanna[72] Diet: Believed to primarily eat worms[72] |
VU
|
| Northern hog badger | A. albogularis (Blyth, 1853) Two subspecies
|
South and East Asia (image includes collaris and hoevenii) |
Size: 55–70 cm (22–28 in) long, plus 11–22 cm (4–9 in) tail[71] Habitat: Forest, bushland, agricultural area, wasteland, and montane grassland[73] Diet: Small vertebrates, invertebrates, and plant material[73] |
LC
|
| Sumatran hog badger
|
A. hoevenii (Blyth, 1853) |
Sumatra | Size: 51–71 cm (20–28 in) long, plus 8–18 cm (3–7 in) tail[71] Habitat: Montane and mossy forests, montane grasslands[74] Diet: Believed to primarily eat invertebrates[74] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian badger | M. leucurus (Hodgson, 1847) Five subspecies
|
Central and east Asia |
Size: 49–70 cm (19–28 in) long, plus 13–21 cm (5–8 in) tail[75] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and forest[76] Diet: Omnivorous; eats fruit, nuts, plants, earthworms, insects, eggs, carrion, and small mammals[76] |
LC
|
| European badger | M. meles (Linnaeus, 1758) Four subspecies
|
Europe (map also includes range of Caucasian badger) |
Size: 56–90 cm (22–35 in) long, plus 11–20 cm (4–8 in) tail[77] Habitat: Grassland, forest, desert, and shrubland[78] Diet: Omnivorous; eats fruit, nuts, plants, earthworms, insects, eggs, carrion, and small mammals[78] |
LC
|
| Japanese badger | M. anakuma Temminck, 1844 |
Japan |
Size: 70–79 cm (28–31 in) long, plus 14–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[79] Habitat: Forest[80] Diet: Primarily eats earthworms and insects, as well as fruit[80] |
LC
|
Subfamily Mellivorinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honey badger | M. capensis (Schreber, 1776) Twelve subspecies
|
Africa, Middle East, and India |
Size: 73–96 cm (29–38 in) long, plus 14–23 cm (6–9 in) tail[81] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, savanna, and desert[82] Diet: Primarily eats smaller mammals[82] |
LC
|
Subfamily Mustelinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Back-striped weasel | M. strigidorsa Gray, 1855 |
Parts of southeast Asia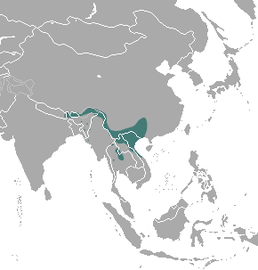 |
Size: 30–36 cm (12–14 in) long, plus 18–20 cm (7–8 in) tail[83] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[84] Diet: Unknown, but believed to eat rodents and insects[83][84] |
LC
|
| Black-footed ferret | M. nigripes (Audubon, 1851) |
Three small areas in central United States |
Size: 50–53 cm (20–21 in) long, plus 11–13 cm (4–5 in) tail[85] Habitat: Shrubland and grassland[86] Diet: Primarily eats prairie dogs[86] |
EN
|
| Egyptian weasel | M. subpalmata Hemprich, 1833 |
Nile river delta in Egypt |
Size: 32–43 cm (13–17 in) long, plus 9–13 cm (4–5 in) tail[87] Habitat: Urban, marine[88] Diet: Primarily eats fruit and vegetables, birds, and insects[89][88] |
LC
|
| European mink | M. lutreola (Linnaeus, 1761) Seven subspecies
|
Scattered parts of west Asia and west Europe |
Size: 35–43 cm (14–17 in) long, plus 15–19 cm (6–7 in) tail[90] Habitat: Inland wetlands[91] Diet: Primarily eats amphibians, crustaceans, fish, small mammals, insects, and birds[91] |
CR
|
| European polecat | M. putorius Linnaeus, 1758 Six subspecies
|
Europe and west Asia |
Size: 29–46 cm (11–18 in) long, plus 8–17 cm (3–7 in) tail[92] Habitat: Inland wetlands, coastal marine, grassland, forest, and shrubland[93] Diet: Primarily eats lagomorphs, rodents, amphibians, and other vertebrates, as well as invertebrates and carrion[93] |
LC
|
| Ferret | M. furo Linnaeus, 1758 |
Worldwide distribution (domesticated) | Size: 20–46 cm (8–18 in) long, plus 7–19 cm (3–7 in) tail[94] Habitat: Domesticated Diet: Primarily eats small mammals |
NE
|
| Indonesian mountain weasel
|
M. lutreolina Robinson, 1917 |
Scattered parts of Indonesia |
Size: 27–33 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 13–17 cm (5–7 in) tail[95] Habitat: Shrubland and forest[96] Diet: Primarily eats rodents, as well as small mammals, birds, amphibians, and eggs[95][96] |
LC
|
| Japanese weasel | M. itatsi Temminck, 1844 |
native to Japan, introduced to Russia (native range in blue, introduced in red (Hokkaido, Sakhalin)) |
Size: 21–36 cm (8–14 in) long, plus 7–16 cm (3–6 in) tail[97] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and forest[98] Diet: Primarily eats rodents, insects, amphibians, and reptiles[98] |
NT
|
| Least weasel | M. nivalis Linnaeus, 1766 Seventeen subspecies
|
Europe, Asia, northern Africa, northern North America |
Size: 11–26 cm (4–10 in) long, plus 1–9 cm (0–4 in) tail[99] Habitat: Forest, inland wetlands, rocky areas, coastal marine, shrubland, and grassland[100] Diet: Primarily eats rodents and other small mammals as well as eggs, lizards, frogs, salamanders, fish, worms, and carrion[100] |
LC
|
| Malayan weasel
|
M. nudipes Desmarest, 1822 Two subspecies
|
Southeast Asia |
Size: 30–36 cm (12–14 in) long, plus 24–26 cm (9–10 in) tail[101] Habitat: Shrubland and forest[102] Diet: Primarily eats rodents, as well as small birds, lizards, and insects[101][102] |
LC
|
| Mountain weasel | M. altaica Pallas, 1811 Four subspecies
|
Central Asia and northern India | Size: 22–29 cm (9–11 in) long, plus 9–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[103] Habitat: Shrubland, rocky areas, and grassland[104] Diet: Primarily eats pikas, rodents, small birds, lizards, and insects[104] |
NT
|
| Siberian weasel | M. sibirica Pallas, 1773 Eleven subspecies
|
North-central and east Asia (native range in green, introduced in red (Japan)) |
Size: 25–39 cm (10–15 in) long, plus 13–21 cm (5–8 in) tail[105] Habitat: Grassland, shrubland, forest, and rocky areas[106] Diet: Primarily eats small mammals, amphibians, fish, carrion, and pine nuts[106] |
LC
|
| Steppe polecat | M. eversmanii Lesson, 1827 Seven subspecies
|
Central Asia and eastern Europe |
Size: 29–56 cm (11–22 in) long, plus 8–18 cm (3–7 in) tail[107] Habitat: Grassland and shrubland[108] Diet: Primarily eats rodents and pikas[108] |
LC
|
| Stoat | M. erminea Linnaeus, 1758 37 subspecies
|
Europe, north Asia, northern North America, and Greenland (native range in green, introduced in red (New Zealand)); map includes range of American and haida ermines |
Size: 17–33 cm (7–13 in) long, plus 4–12 cm (2–5 in) tail[109] Habitat: Shrubland, inland wetlands, grassland, rocky areas, and forest[110] Diet: Primarily eats small mammals, as well as fruit, earthworms, insects, eggs, and birds[110] |
LC
|
| Yellow-bellied weasel | M. kathiah Hodgson, 1835 Two subspecies
|
Himalayan mountains and east-southeast Asia |
Size: 25–27 cm (10–11 in) long, plus 12–15 cm (5–6 in) tail[111] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[112] Diet: Primarily eats rodents, as well as birds and small mammals[111][112] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon weasel
|
N. africana (Desmarest, 1818) Two subspecies
|
Amazon basin |
Size: 41–52 cm (16–20 in) long, plus 16–21 cm (6–8 in) tail[113] Habitat: Inland wetlands and forest[114] Diet: Unknown[115][114] |
LC
|
| American mink | N. vison (Schreber, 1777) Fifteen subspecies
|
Canada and United States; introduced to large areas in South America, Europe, and Asia (native range in red (North America), introduced in pink) |
Size: 31–45 cm (12–18 in) long, plus 14–25 cm (6–10 in) tail[116] Habitat: Inland wetlands, forest, and shrubland[117] Diet: Primarily eats fish, amphibians, crustaceans, muskrats, and small mammals[117] |
LC
|
| Colombian weasel
|
N. felipei (Izor and Torre, 1978) |
Small area of northwest South America |
Size: 32–39 cm (13–15 in) long, plus 10–14 cm (4–6 in) tail[118] Habitat: Inland wetlands and forest[119] Diet: Unknown, but believed to eat fish, small mammals, and insects[120][119] |
VU
|
| Long-tailed weasel | N. frenata (Lichtenstein, 1831) 42 subspecies
|
North America, Central America, and northern South America |
Size: 28–42 cm (11–17 in) long, plus 11–30 cm (4–12 in) tail[121] Habitat: Inland wetlands, grassland, and shrubland[122] Diet: Primarily eats rodents and other small mammals[122] |
LC
|
| Sea mink†
|
N. macrodon (Prentiss, 1903) |
formerly northern New England coast in United States, Maritime Provinces in Canada |
Size: Estimated to have been around 91 cm (36 in) long, plus 25 cm (10 in) tail[123] Habitat: Intertidal marine, neritic marine, and coastal marine[124] Diet: Primarily ate fish as well as molluscs[124] |
EX
|
Subfamily Taxidiinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American badger | T. taxus (Schreber, 1777) Five subspecies
|
Mexico, United States and southern Canada |
Size: 42–72 cm (17–28 in) long, plus 10–16 cm (4–6 in) tail[125] Habitat: Forest, grassland, and shrubland[126] Diet: Primarily eats fossorial rodents, as well as scorpions, insects, snakes, lizards, and birds[126] |
LC
|
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.























































