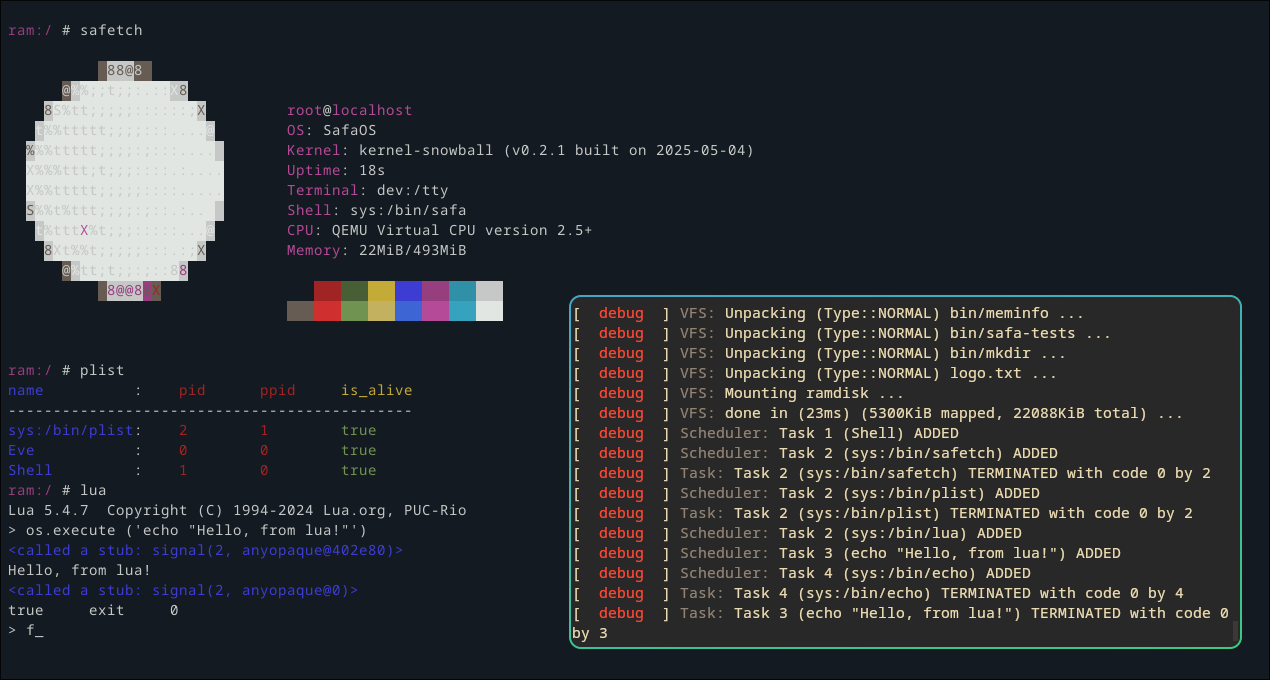
An open-source non-Unix-like OS, written from scratch in Rust for fun.
The crate at the root of the project is called safa-helper it is basically the build system.
you need:
- git
- xorriso
- make
- cargo
- libcurl (should be bundled by default in most operating systems including windows)
First you have to run
cargo run init
once every rust libstd update (or if you are not actively working on the project just once every git pull would work).
If you want to cross compile SafaOS for an architecture other then your host's run
cargo run init -a [arch]
currently arch can either be x86_64 or aarch64.
then to build run
cargo run build
(the -a|--arch flag works for build too)
This should make an iso with the path: out/safaos.iso if successful,
You can also find pre-built artifact isos built using github actions, check the latest successful build for the main branch.
you'll need:
- qemu-system-[arch]: where arch is either
x86_64oraarch64.
cargo run -- --no-kvm
(the -a|--arch flag is also available for running, if you want to use it you must likely want to provide the --no-kvm flag too)
or run with kvm (faster but kvm might not be available or broken)
cargo run
otherwise you have the iso out/safaos.iso feel free to do whatever you want with it,
you also have
you can also use the safa-helper to debug:
cargo run -- --debugger --no-kvm
(doesn't work with kvm)
and then connect to port 1234 with a gdb client i recommend using rust-lldb.
$ cargo run help
The SafaOS's build system and helper tools
Usage: safa-helper [OPTIONS] [COMMAND]
Commands:
init Initializes the submodules and installs the SafaOS's toolchain (rustc target)
build Builds a SafaOS iso
run Builds and Runs a normal SafaOS iso, requires qemu (default)
test Builds and runs a test SafaOS iso, requires qemu
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
Options:
--no-kvm runs with kvm disabled
--no-gui runs with gui disabled
--debugger runs with debugger enabled on port 1234
--qemu-args <QEMU_ARGS> [default: ]
-o, --output <OUTPUT> The final output of the built iso the default is out/safaos.iso for normal isos and out/safaos-tests.iso for test isos
-v, --verbose
-a, --arch <ARCH> [default: x86_64] [possible values: aarch64, x86_64]
-h, --help Print help
-V, --version Print version
you'll need:
- qemu-system-[arch]: where arch is either
x86_64oraarch64.
to test SafaOS for the current host, run:
cargo run test --no-kvm
or use the -a|--arch flag to test a specific arch, you can also omit --no-kvm if kvm is available.
or to test all architectures (requires all qemu-system-[arch] variants) run:
cargo test
then the tests will be ran for all architectures with no kvm and no gui.
crates-user/: contains userspace programs written in rust, they are compiled and then copied to the ramdisk as sys:/bin/, any rust binary crate added to this directory would be automatically detected, compiled and bundled to the ramdisk by the safa-helper.
crates: contains the kernel and other kernel-related crates (only the kernel crate is detected by the safa-helper).
ramdisk-include: anything put in this directory will be included in the ramdisk at sys:/ by the safa-helper.
common: some constants and files that are used by the build system.
src: the source of the SafaOS build system and helper utils aka safa-helper.
Check FEATURES.md.
you can also check crates-user/ for examples of programs written in rust.
Aside from the rust stdandard library another method to interact with the kernel is through the safa-api which provides low-level wrapper functions around the syscalls, and also some high-level wrappers (such as a userspace allocator which is a very high-level wrapper around the sbrk syscall, ofc the raw sbrk syscall is still exposed).
check out CONTRIBUTING.md
currently uses the limine bootloader. Thanks to the developers of:
- MinOS, TacOS, and BananaOS for helping develop this.
- StelluxOS for their awesome OS and XHCI tutorial, which helped me implemented USB support.