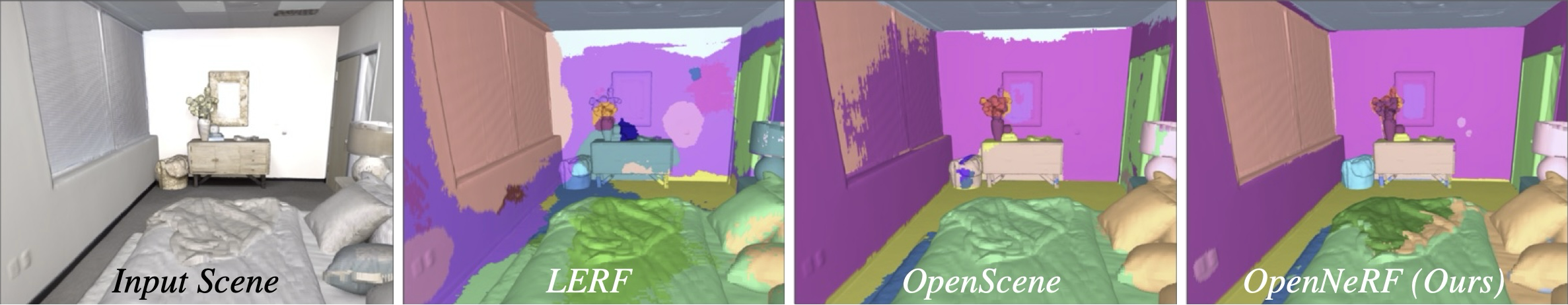
Francis Engelmann, Fabian Manhardt, Michael Niemeyer, Keisuke Tateno, Marc Pollefeys, Federico Tombari
Paper | Project Page | Demo
After installing conda (see here), setup the conda environment:
conda create --name opennerf -y python=3.10
conda activate opennerf
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
conda install nvidia/label/cuda-12.1.1::cuda
conda install pytorch==2.1.2 torchvision==0.16.2 torchaudio==2.1.2 pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
python -m pip install ninja git+https://github.com/NVlabs/tiny-cuda-nn/#subdirectory=bindings/torch
python3 -m pip install 'tensorflow[and-cuda]'
git clone https://github.com/opennerf/opennerf
cd opennerf
python -m pip install -e .
pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall pillow
ns-install-cli
The datasets and saved NeRF models require significant disk space. Let's link them to some (remote) larger storage:
ln -s path/to/large_disk/data data
ln -s path/to/large_disk/models models
ln -s path/to/large_disk/outputs outputs
Download the OpenSeg feature extractor model and unzip it into ./models.
cd models
wget https://geometry.stanford.edu/projects/openseg/openseg_exported_clip.zip
unzip openseg_exported_clip.zip
Download the Replica dataset pre-processed by NICE-SLAM and transform it into nerfstudio format using these steps:
cd data
wget https://cvg-data.inf.ethz.ch/nice-slam/data/Replica.zip
unzip Replica.zip && mv Replica replica
cd ..
python datasets/preprocess.py --dataset-name=replica
Set up the SceneFun3D repository to download the dataset:
git clone https://github.com/SceneFun3D/scenefun3d.git
cd scenefun3d
conda create --name scenefun3d python=3.8
conda activate scenefun3d
pip install -r requirements.txt
Download the dataset (make sure to put the correct download_dir):
python -m data_downloader.data_asset_download --split test_set --download_dir /path/to/large_disk/data --visit_id 421372 --download_only_one_video_sequence --dataset_assets arkit_mesh hires_poses transform laser_scan_5mm
The preprocessed LERF dataset is available from the official repository.
This repository creates a new Nerfstudio method named "opennerf". To train with it, run the command:
ns-train opennerf --data [PATH]
See .vscode/launch.json for specific training examples.
To view the optimized NeRF, you can launch the viewer separately:
ns-viewer --load-config outputs/path_to/config.yml
Adapt the global variables CONDA_DIR and PREFIX in train_eval_replica_semantics.py. Then run it:
python scripts/train_eval_replica_semantics.py
This version of the code corresponds to entry (2) "Render & Project" in Table 2 of the paper and produces the following 3D semantic segmentation scores on the Replica dataset:
| All | Head | Common | Tail | |||||
| mIoU | mAcc | mIoU | mAcc | mIoU | mAcc | mIoU | mAcc | |
| Run 0 | 18.74% | 31.87% | 30.26% | 43.89% | 20.07% | 33.52% | 5.88% | 18.19% |
| Run 1 | 19.68% | 32.68% | 30.76% | 44.70% | 20.84% | 34.16% | 7.43% | 19.17% |
| Run 2 | 18.80% | 31.72% | 30.36% | 44.02% | 19.63% | 32.71% | 6.41% | 18.43% |
If you find our code or paper useful, please cite:
@inproceedings{engelmann2024opennerf,
title = {{OpenNeRF: Open Set 3D Neural Scene Segmentation with Pixel-Wise Features and Rendered Novel Views}},
author = {Engelmann, Francis and Manhardt, Fabian and Niemeyer, Michael and Tateno, Keisuke and Pollefeys, Marc and Tombari, Federico},
booktitle = {International Conference on Learning Representations},
year = {2024}
}