- Infrastructure as a code
- Infrastructure can be in different platforms/providers and using terraform we can create infrastructure in one place as a code
- Terraform can be used with any cloud provider
- Ansible module can be used to create infra.
- Ansible used for configuration management
- Terraform can be used for infrastructure management
- Use terraform when there is no infra. and you have to design infra. from scratch
- Now infra is ready and you want to deploy your application, so configuration for these can be done using Ansible or puppet.
- Terraform maintains the state of the resource created.
- To delete infra. in ansible you have to write a new file for the same, but not the same for terraform.
- OS level configuration - Ansible
- Terraform - Infra creation
- Install Terraform
- Install
Hashicorp TerraformVSCode extension - Configure path
// block "label1" label2 {
// identifier = expression
//}
// this is first comment
# this is second comment
terraform plan
filename.tf.json- don't write in this format
.tfuse more.tf.json- when creating web application, json format is used for better automation
- Problem may arise when creating multiple infra from multiple blocks
- may cause problems in complex infra
- destructuring it is a better solution
- concern of separation is needed
- Terraform runs all
.tffiles in the current directory - Files load in alphabetical order
variable abc {}var.abc- dont use it inside string
- inside string, use
${abc} - use file destructer too
terraform plan -var "username=Barun"
variable username {
default = "Barun"
}terraform plan -var "username=Barun" -var "age=20"
- List
- List of string
- Object
- Docs
type=variableType
type = list- enter list variable in command line:
- `["A", "B", "C"]
terraform plan -var 'users=["A", "B", "C"]'- [Docs]https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/language/functions
value="${join(",", var.users)}loweruppertitlezipmap(imp.)
type = maplookup
terraform.tfvarsterraform plan --help | lessterraform plan -var-file=development.tfvars
export TF_VAR_variableName=valueterraform plan -lock=false
- Github Provider
- Github Create Repository
terraform providersterraform initfile filename_vxxx
terraform planterraform apply- authentication error- use github personal access token
- test repo
terraform.tfstate- Dont manually udpate
tfstatefile terraform plan- compares terraform.tf and terraform.tfstate file and creates resource not present in.tfstatefile
- Dont manually udpate
terraform apply --auto-approveterraform.tfstate.backup- backup the resource state before you appliedterraform applyterraform destroyterraform destroy --helpterraform destroy --target github_repository.terraform-second-repoterraform validateterraform refresh- updates.tfstateby fetching manually update resource detailsterraform show- output
terraform output resource_name
terraform console- read variables from current directory in a consolevar.variableName
terraform fmt- does a formatting of the terraform variables
1. EC2 instance
2. instances
3. Ubuntu 18.04 - AMI ID (varies according to region)
- copy AMI code
4. t2 micro, 1 instance - default
5. storage - default
6. tag: name: testVM
7. configure-security - only ssh, port 22
8. Review and Launch
9. create new key pair
10. `chmod 400 xyz.pem`
11. `ssh -i "xyz.pem" ubuntu@abc.compute-1.amazonaws.com`
1. `provider aws {....}`
2. [Docs](https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs)
3. IAM - Add user
4. Create Key Pair - Copy AMI, Secret Key, Access Key
- Give administrator access first
5. `terraform init`
6. `terraform plan`
7. `terraform apply --auto-approve`
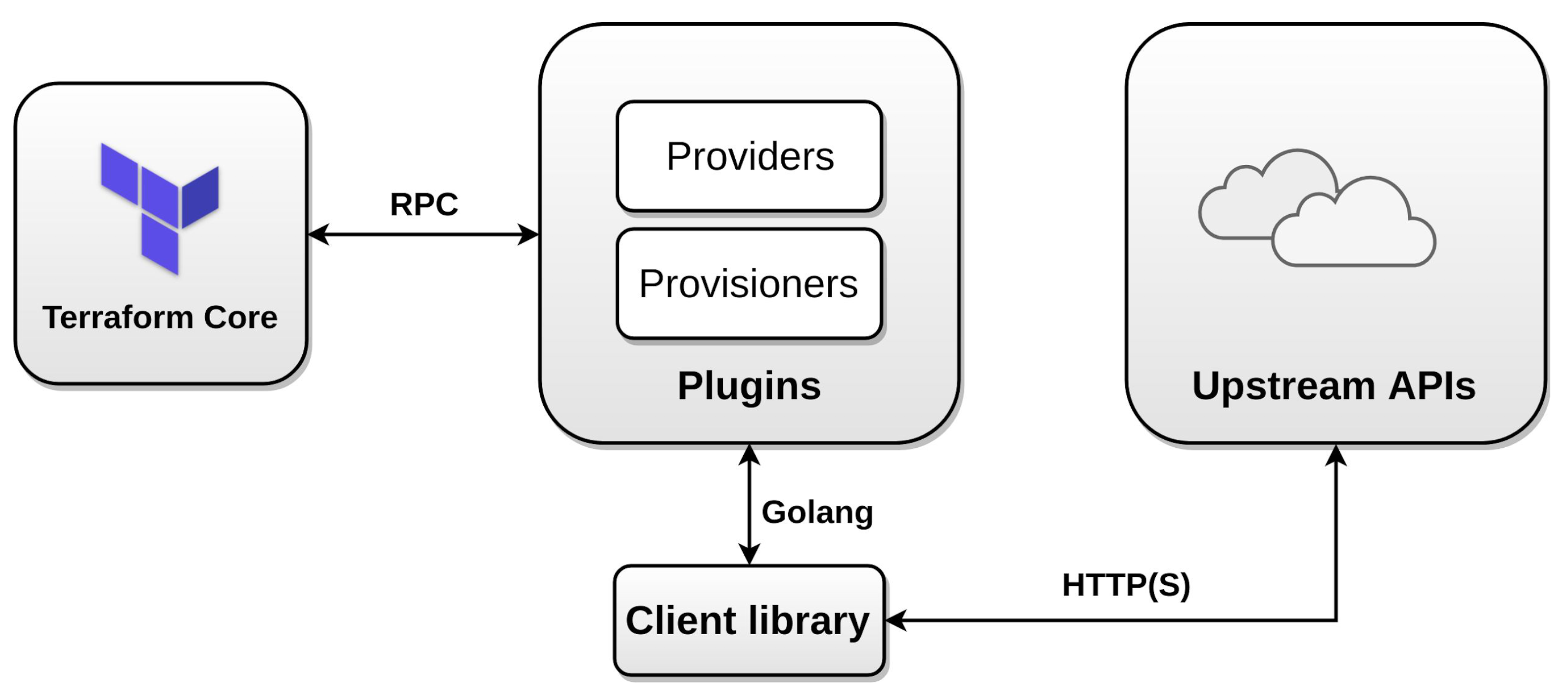
8. Terraform divided into two parts:
- Core
- Plugin
9. `terraform show`
10. `terraform fmt`
11. Problems:
- Default security group
- No SSH key pair for connection
12. `terraform destroy`
-
Tasks:
- ssh-key -> first-key
- assign first-key to newly created instance
- create a security group
- assign that group to instance
- Install nginx
- /var/www/html/index.nginx-default.html -> hey, Barun
- ssh-key -> first-key
-
Steps:
ssh-keygen -t rsa- location - default
- key-value pair
- attach ssh public/private key to VM instance
- if not able to SSH, problem with security group
- creating security group using terraform
- Attach security group to instance
ssh -i privatekeyfile username@ip
sudo -iapt-get updateping 8.8.8.8- can't be accessed incoming from outide
- only outgoing from anywhere
- add egress block
- now it will work
- install nginx - check if it is working
- IP address to access - public ip address
- Project structure
export TF_VAR_access_key=...export TF_VAR_secret_key=...env | grep -i access_key
- Added shellscript to automate nginx installation and editing html file
- shellscript directly automating not a good practice
- sometimes error may occur and you wont know
- Best approach - use configuraiton management tool
- Other ways - Terraform Provisioners (Not recommended)
dynamic "abc" {
for_each=[a,b,c,d]
iterator=x
content{
data=x.value
}
}terraform taint resource.name- shows the resource is damaged
- will destroy/delete old resource, then recreate the new ones
- not recommended
- use
terraform apply --refresh
- three types:
- file
- local-exec
- remote-exec
- If provisioner not runned successfully, then that particular resource will be marked as
tainted. - Infinite cycle on calling its own resource
- use
self
- use
- File Provisioner:
- source
- destination
- connection
- content
- copy file
- text
- copy folder
local-exec:- command runs on local machine where terraform is running
- arguments:
- command
- working_dir
- interpreter
- environment
when
remote-exec:- Failure Behavior:
continuefail
on_failure: continue- runs commands inside resource group
- types:
- inline
- terraform don't change/store the state of scripts/configuration etc.
- Failure Behavior:
- Image ID
amican be changed by AWS - its not static - so instead of giving ami, you tell AWS the configurations:
- root device type
- storage type
- Virtualization type, etc.
- It returns a image type using DataSource
- Doc
- Working in team
- running before terraform commands - plan/apply/etc. check if specific terraform version exists or not
- Terraform version constraints
- can't define variables
- only accept hard-coded variables
- show allocated resources in graph format
sudo apt install graphvizterraform graph | dot -Tpdf graph.pdf
dev.terraform.tfvarsprod.terraform.tfvarsterraform plan --var-file=dev.terraform.tfvarsterraform plan --var-file=prod.terraform.tfvars
- List default workspace
terraform workspace list
terraform workspace new workspaceNameterraform workspace showterraform.tstate.d- contains directory of each workspace
terraform workspace select workspaceNameterraform workspace list- workspace - apply tfstate file forms inside separate directory inside tf.state.d folder
terraform workspace delete workspaceNameOtherThancurrentWorkspace- can't delete default workspace
- Reusuable code
terraform init- initializer modules, providers, backends
- Terraform s3 backend
- working in team may replace the present infra
- keep the tfstate file in remote location
- dont keep inside
git - not a best practice
- many times developer forget to pull/push
- Terraform provide some backends to resolve the issue
- any backend install - take care AWS/GC 56AF P/etc. CLI is already installed
- S3 bucket to store tfstate file
- take care of s3 bucket cli access
terraform init -migrate-state- stored in local system
- when two users updates tfstate file - might change file
- how to solve this
- adding an entry that a particular user is changing file and others cant
- using DynamoDB
- in S3 backend, you can also use versioning
- will show error if at same time, another user does
terraform apply