- NVM and node version 8.
- yarn
- AWS CLI
- BASH
- Docker (only required for testing)
- docker-compose (only required for testing
pip install docker-compose)
Install the correct node version:
nvm install
nvm use
Ensure that the aws cli is configured and that the default output format is either JSON or None:
aws configure
We use Lerna to manage multiple Cumulus packages in the same repo. You need to install lerna as a global module first:
$ yarn global add lerna
We use yarn for local package management
$ yarn install
$ yarn ybootstrap
Building All packages:
$ yarn build
Build and watch packages:
$ yarn watch
LocalStack
AF8BLocalStack provides local versions of most AWS services for testing.
The LocalStack repository has installation instructions.
Localstack is included in the docker-compose file. You only need to run the docker-compose command in the next section in order to use it with your tests.
Turn on the docker containers first:
$ docker-compose up local
If you prefer to run docker in detached mode (i.e. run containers in the background), run:
$ docker-compose up -d local
Run the test commands next
$ export LOCALSTACK_HOST=localhost
$ yarn test
Run end to end tests by
$ yarn e2e
- Run
./bin/prepare - Deploy your instance integrations on aws and run tests by following the steps here
Code coverage is checked using nyc. The CircleCI build tests coverage. A summary can be viewed in the build output. Detailed code coverage in html can be found by going to the Artifacts tab and navigating to index.html in the coverage folder. Clicking on index.html will take you to an html page showing code coverage for each individual file.
The yarn test command will output code coverage data for the entire Cumulus repository. To create an html report, run nyc report --reporter html and open the index.html file in the coverage folder.
To run code coverage on an individual package during development, run npm run test-coverage. This will output the coverage in the terminal. An html report can be created using nyc report --reporter html as described above.
This project uses eslint to check code style and quality. The configured eslint rules can be found in the project's .eslintrc.json file.
In an effort to gradually reduce the number of eslint errors in our codebase,
we are using a script called eslint-ratchet. It runs eslint against the
repo and compares the number of errors to the previous number of errors. The
previous number of errors is stored in the .eslint-ratchet-high-water-mark
file, and tracked in git. If the script is run and the number of errors has
been reduced, the new, lower score is stored in
.eslint-ratchet-high-water-mark and should be committed into git. If the
number of errors has increased, the script will fail and tell you that the
number of errors has increased.
To run the script, simply run ./bin/eslint-ratchet from the top of the
cumulus repository.
The eslint-ratchet script is also part of our CircleCI build. If the number
of eslint errors that CircleCI finds has increased, it will fail the build. If
the number of errors has decreased from what is stored in
.eslint-ratchet-high-water-mark, it will also fail the build. In that case,
run ./bin/eslint-ratchet and commit the new-and-improved
.eslint-ratchet-high-water-mark file.
To help prevent unexpected build failures in CircleCI, I suggest adding a
local post-commit hook that will run eslint-ratchet after every commit. This
will not cause your commits to fail if the score has increased, but it will
let you know that there is a problem. To set up the post-commit hook, create a
file called .git/hooks/post-commit which contains:
#!/bin/sh
set -e
echo "Running ./bin/eslint-ratchet"
./bin/eslint-ratchet
Make sure the hook is executable with chmod +x .git/hooks/post-commit
This idea of ratcheting down the number of errors came from Vince Broz's excellent quality gem.
Create a new folder under packages if it is a common library or create folder under cumulus/tasks if it is a lambda task. cd to the folder and run npm init.
Make sure to name the package as @cumulus/package-name.
We use a global versioning approach, meaning version numbers in cumulus are consistent across all packages and tasks, and semantic versioning to track major, minor, and patch version (i.e. 1.0.0). We use Lerna to manage our versioning. Any change will force lerna to increment the version of all packages.
Read more about the semantic versioning here.
When changes are ready to be released, the Cumulus version number must be updated using semantic versioning.
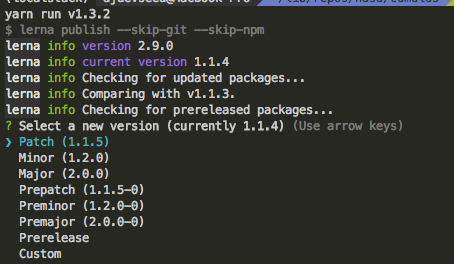
Lerna handles the process of deciding which version number should be used as long as the developer decides whether the change is a patch or a minor/major change.
To update cumulus' version number run:
$ yarn update
You will be prompted to select the type of change (patch/minor/major). Lerna will update the version of all packages after the selection.
Your next steps should be:
- Commit the package version updates that are made by Lerna.
- Update the CHANGELOG.md. Put a header under the 'Unreleased' section with the new version number and the date.
- Add a link reference for the github "compare" view at the bottom of the CHANGELOG.md, following the existing pattern. This link reference should create a link in the CHANGELOG's release header to changes in the corresponding release.
- Update the Cumulus package versions in the example/package.json
Commit all changes and open a PR.
The version number updates should be put in a PR and committed to master along with the changelog updates. After merging to master, tag the master branch with a release using the new version number.
Release PRs MUST be named with release- prefix. This will kick off the AWS integration tests in the CI process and ensures that package updates are fully tested on AWS before publication to NPM.
All packages on master branch are automatically published to NPM.
Follow the following steps to publish to NPM:
- Create a new branch from
masterand call itrelease-version-<version_number> - Run
yarn update - Select the correct version upgrade type (e.g. major/minor/patch)
-
Update CHANGELOG.md
-
Push to Github
-
Create a new git tag
$ git tag -a v1.x.x -m "version 1.x.x release"
-
Push the tag to github
$ git push origin v1.x.x
-
Create a PR against the
masterbranch -
After the PR is merged, update the (tag) and give a proper title and copy the release details from the CHANGELOG.md to the release
$ lerna exec -- rm -rf ./package-lock.json
$ yarn clean